
 share
share
Reading Time
7 minutes.
TL&DR
- DePIN (Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks) extends blockchain beyond software by decentralizing the physical internet layer: storage, bandwidth, and compute.
- It fixes Web3's main gap by letting individuals power and earn from real infrastructure instead of relying on centralized clouds.
- Titan Network is a leading DePIN example, rewarding users for sharing digital resources while offering enterprises decentralized cloud, CDN, and compute services, representing a natural evolution of the cloud model.
Introduction: A Decade of Decentralization
Just over a decade ago, blockchain introduced the world to a radical idea: You don't need a central authority to coordinate value.
It was soon followed by Ethereum, which expanded that vision. Now, you could not only send money but also build applications, execute contracts, and run digital economies without banks, governments, or tech giants in the middle.
This led to the rise of Web3, a movement to return control of the internet to users through wallets, tokens, and decentralized apps (dApps).
And it made real progress:
- People could own digital assets (NFTs, tokens)
- Communities could govern platforms (DAOs)
- Developers could launch permissionless ecosystems (DeFi, open dApps)
But while Web3 reimagined ownership and logic, it didn't change the physical reality of the internet: The infrastructure still ran on the same centralized rails.
Now, that's beginning to shift.
Enter DePIN Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks. A new wave of blockchain-powered platforms is bringing decentralization down to the physical layer into the wires, routers, and hard drives that make the internet run.
1. A Brief History: From Bitcoin to Web3
To understand why DePIN matters, it helps to zoom out and look at the internet's broader evolution.
Web1 (1990s–early 2000s): Read
The early internet was open but basic. Static websites let users read content, but not interact. Infrastructure was relatively decentralized hosted across universities, ISPs, and individual servers.
- Think: Personal blogs, web forums, early email
- Users were consumers; corporate platforms were limited
Web2 (2005–present): Read + Write
The rise of platforms like Facebook, YouTube, Amazon, and Google changed everything. Users could now upload content and build audiences, but always through centralized gatekeepers.
- Big Tech controlled the data, set the rules, and extracted the value
- Cloud platforms like AWS and GCP became the internet's default infrastructure
Web3 (2015–today): Read + Write + Own
Then came blockchains, starting with Bitcoin in 2009 a decentralized way to move money without banks. This marked the beginning of a new era: one where users could interact with the internet not just as consumers, but as owners and participants in the systems they used.
This sparked a new era of decentralized innovation:
- Bitcoin → trustless digital money
- Ethereum → programmable, decentralized apps
- DeFi → peer-to-peer lending, trading, and saving
- NFTs → verifiable digital ownership
- DAOs → decentralized governance
Web3 gave users control over their assets, identity, and participation. It reimagined how value flows online without centralized institutions.
But as you'll see in the next section, this revolution largely stopped at the application layer. The physical infrastructure, the cloud servers, bandwidth, and compute remained centralized.
2. The Problem Web3 Didn't Solve
Web3 promised a more open and decentralized internet but one critical layer remained centralized: infrastructure.
Most dApps still rely on:
- Frontends hosted on AWS or Google Cloud
- APIs and services managed by private companies
- Data routing through Cloudflare or similar CDNs
- IPFS for file storage but pinned by centralized services
In other words, Web3 decentralized the software but not the hardware. This isn't a flaw in blockchain. It's a blind spot. Web3 focused on logic, value, and governance, but didn't address the physical backend where data is stored, how it's transmitted, and which machines are powering the system.
This creates real-world vulnerabilities:
- Single points of failure (a cloud outage can take entire dApps offline)
- Opaque pricing from cloud vendors
- Limited infrastructure access in emerging regions
- Control bottlenecks even in supposedly decentralized apps
That's the gap DePIN is filling.
Read: What is DePIN? A Complete Beginner's Guide →
3. What Makes DePIN Different
While Web3 reimagined how we own and interact with digital value, it largely stopped at the application layer wallets, tokens, smart contracts, and decentralized apps. DePIN goes deeper. It tackles the infrastructure layer: the servers, bandwidth, storage, and compute that power the internet itself.
Think of it this way:
- If Web3 builds the apps marketplaces, social networks, smart contracts
- DePIN builds the roads, rails, and utilities; those apps run on storage networks, bandwidth routes, and distributed compute.
In other words, DePIN is the infrastructure layer Web3 was missing.
It brings the same principles that made blockchains work: open participation, transparent verification, and tokenized incentives to the physical machinery of the internet.
From Users to Infrastructure Providers
At a high level:
- Web3 lets you own your data, your tokens, your rules
- DePIN lets you own the infrastructure and earn for powering it
This changes the game for how services are delivered:
- Apps no longer need Amazon or Google to scale
- Communities in underserved regions can host and benefit from infrastructure locally
- Contributors around the world can monetize digital resources they already own
And this isn't just theoretical. DePIN networks are live today running on real devices owned by regular people. If you have:
- Spare storage on a hard drive
- Idle bandwidth on your home internet
- IP Leasing
- Unused GPU cycles on your laptop or desktop
...you can contribute it to a DePIN network, and get rewarded when that capacity is used. Your device becomes a micro–data center part of a distributed, decentralized cloud that delivers real services to real users.
4. Why This Shift Matters
This isn't just a technical upgrade, it's a restructuring of how the internet is built, accessed, and shared.
For decades, cloud infrastructure has followed a centralized model: large corporations build expensive data centers, set the pricing, and control access. Users whether they're individuals, startups, or even Web3 projects simply pay to use those services.
DePIN flips that model.
It introduces a distributed, community-driven approach where anyone can participate not just as a user, but as a contributor to the infrastructure itself. Here's how the models compare:
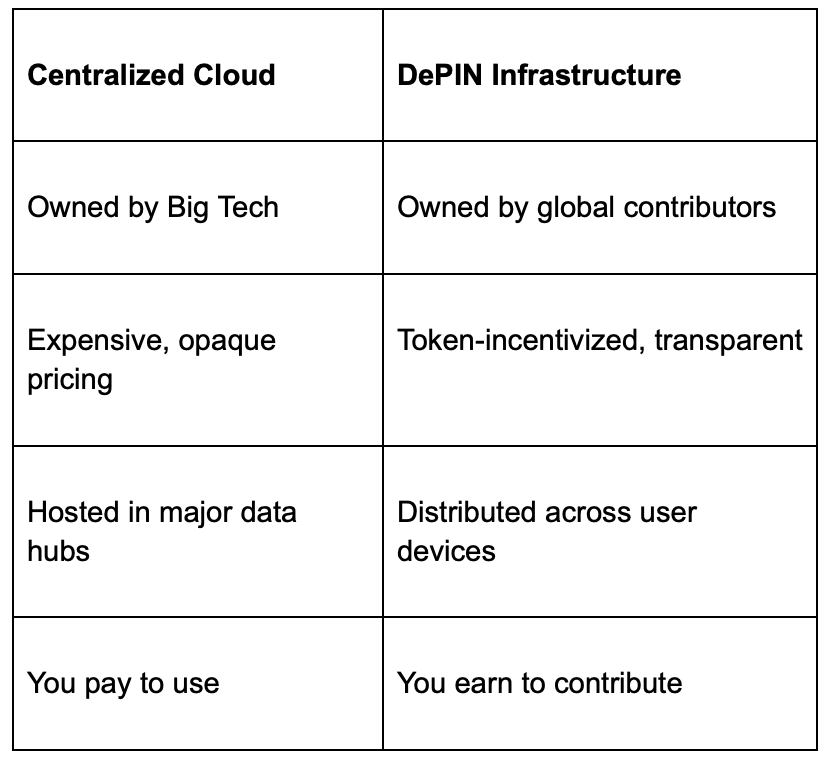
Instead of building more massive data centers, DePIN networks tap into the idle digital resources already all around us: laptops, routers, external drives, GPUs, and more.
Just like Airbnb turned homes into hotels, DePIN turns unused device capacity into real infrastructure and shares the value with the people who power it.
This shift matters because it:
- Expands access to underserved regions and users
- Reduces costs for developers and enterprises
- Improves resilience through decentralization
- Creates income opportunities based on utility, not speculation
5. The Role of Blockchain in DePIN
At this point, you might be wondering: If DePIN is about infrastructure, why is blockchain still involved?
The answer lies in what it takes to make a decentralized system work especially when it's made up of thousands (or millions) of independently owned devices.
To function at scale and without a central authority, DePIN networks need three things:
- Verification: Did this device actually store the file? Did it deliver data as promised? Did it stay online and perform as expected?
- Incentives: Who deserves to be rewarded? How much should they earn? What ensures they act honestly and contribute reliably?
- Transparency: Can participants trust the network without needing to trust each other? Can contributions be verified by anyone?
This is where blockchain comes in.
Blockchains don't host infrastructure but they're crucial for making DePIN work. They provide a shared, tamper-proof ledger that does three essential things:
- Tracks what resources were contributed, by whom, and when
- Coordinates which nodes should handle which tasks
- Rewards contributors automatically, based on verified performance
Think of blockchain as the operating system for decentralized infrastructure. It keeps score, distributes payment, and enforces rules without needing a central referee.
It also ensures that:
- No one can game the system
- Everyone sees the same information
- The network can scale globally while staying trustless
DePIN is not trying to replace blockchain. It's extending its usefulness into the real world turning decentralized ledgers into the backbone for decentralized infrastructure.
- Web3 made decentralized finance possible.
- DePIN makes decentralized infrastructure usable.
6. Where Titan Network Fits In
Titan Network is part of this new generation of infrastructure and one of the few platforms delivering a full DePIN solution that works for both individuals and enterprises.
For contributors, Titan makes it easy to:
- Share unused storage, bandwidth, or compute power
- Join the network through lightweight apps no mining rigs, no technical expertise required
- Earn $TNT tokens based on actual usage and performance
For businesses, Titan offers decentralized alternatives to traditional cloud services:
- Content delivery via a peer-powered CDN
- Scalable compute for AI and edge applications
- Secure IP leasing through a global pool of residential nodes
Titan doesn't just follow DePIN principles it operationalizes them. By combining blockchain coordination with real-world utility, it shows what's possible when infrastructure is owned, powered, and rewarded by the network itself.
7. Why This Is the Natural Evolution of Cloud
The history of the internet has always moved in cycles from open to closed, from decentralized to centralized, and now, back again.
- Email started peer-to-peer. Then Gmail centralized it.
- Web hosting used to be self-managed. Then AWS became the standard.
- Apps were once downloaded and owned. Now they live in the cloud rented, metered, and controlled.
Today, that model is being reimagined.
- People are once again hosting their own infrastructure
- Communities are coordinating and powering digital services
- Value is flowing not just to providers but to participants
DePIN doesn't reject the cloud; it rebuilds it from the ground up, using distributed networks, user-owned devices, and blockchain-based coordination.
And platforms like Titan Network represent the next logical step where infrastructure is not only decentralized, but accessible, usable, and economically aligned with the people who power it.














